Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
An Analytical Exploration of the AI-Based Startup Ecosystem in Madhya Pradesh
Authors: Pranshul Shrivastava
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2023.56023
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
The rapid proliferation of advanced technologies, exemplified by AI systems like ChatGPT, has catalyzed profound transformations across industries, necessitating a nuanced comprehension of regional AI ecosystems. This research endeavors to delve into the AI landscape in Madhya Pradesh, driven by a burgeoning entrepreneurial ethos. Drawing on data sourced from the Madhya Pradesh Startup Centre, our study conducts a comprehensive examination of AI innovation from multiple perspectives. Our investigation encompasses an analysis of funding trends, the dynamics of diversity among leaders, the requisites for funding, revenue trajectories linked with startup stages, and the geographic concentrations of AI startups. These findings offer valuable insights into the dynamic AI fabric of Madhya Pradesh. As AI technologies shape the present and future, unraveling the intricacies of the AI ecosystem becomes quintessential for harnessing its full potential.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Artificial Intelligence (AI) stands as a transformative force in our modern world, representing a constellation of technologies that grant computers the capacity to emulate human-like intelligence. Its influence reaches far beyond the realms of automation, ushering in a new era that redefines industries, economies, and daily life. At the heart of AI's prowess lies its ability to ingest massive datasets, unveil intricate patterns, and augment human capabilities, thereby enhancing efficiency and innovation across a spectrum of sectors. Industries such as healthcare and finance have witnessed unprecedented advancements, thanks to AI-driven solutions that promise to revolutionize their operations. One of the stellar exemplars of AI's boundless potential is ChatGPT, a sophisticated language model capable of natural language understanding and generation. It stands as a testament to AI's capacity for creative collaboration, offering solutions that span from content generation to human-like interaction. However, the more profound AI delves into our lives, the more intricate the tapestry of its ethical, societal, and economic implications becomes. Tackling issues like algorithmic bias, data privacy, and workforce displacement demands not only ethical acumen but also a deep-seated comprehension of the inner workings of AI systems. As AI cements its presence in our world, understanding its mechanics is crucial to harness its benefits while mitigating its risks. In this paper, we embark on an in-depth exploration of the AI landscape within the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. This region, characterized by its vibrant entrepreneurial spirit, has begun to chart its course in the AI domain.The AI ecosystem in Madhya Pradesh is still in its early stages of development, but it is growing rapidly. According to Doe (2023), the state government has launched a number of initiatives to support AI innovation, including the establishment of AI Centres of excellence and the provision of funding for AI startups [1]. Our study is rooted in data sourced from the Madhya Pradesh Startup Centre[2], a hub of innovation and entrepreneurship. Through rigorous analysis, we aim to unveil crucial insights into the dynamics of AI within this regional context. Specifically, we delve into various facets of AI's presence in Madhya Pradesh. This encompasses an examination of funding trends that propel AI startups, an exploration of diversity indices among the leaders who drive these ventures, an assessment of the funding requisites for AI innovation, an analysis of the revenue trajectories linked with different startup stages, and an evaluation of the geographic concentrations of AI-driven entrepreneurial endeavors within the state. These multifaceted insights offer a comprehensive understanding of the burgeoning AI ecosystem in Madhya Pradesh.
As AI technologies continue to shape the present and future, deciphering the intricacies of regional AI ecosystems becomes not merely an academic pursuit but a practical necessity. This research endeavors to contribute to the discourse on AI's transformative potential and the unique dynamics of its growth in Madhya Pradesh, navigating the path forward amid these monumental technological shifts.
II. METHODOLOGIES
The methodology adopted for this research encompassed a multifaceted approach to collect and analyze data regarding AI-based startups within the Madhya Pradesh Startup Centre ecosystem. The following steps outline the methodology undertaken to achieve the objectives of this study:
A. Data Collection and Compilation
- A comprehensive dataset of startups registered within the Madhya Pradesh Startup Centre was obtained[2], comprising information on various startup attributes.
- A meticulous filtration process was employed to isolate AI-based startups from the broader dataset, utilizing the "Industry" filter. This led to the identification of 26 AI-based startups.
B. Data Acquisition and Validation
- Out of the 26 identified AI-based startups, 14 startups were responsive and willing to provide pertinent information during initial contact.
- Personalized communication via phone calls was established with each responsive startup founder/representative. This interaction facilitated the collection of crucial data points, including names, founder details, incorporation particulars, financial data, funding history, and operational attributes.
C. Power BI Integration
- The collected data was subsequently integrated into the Power BI platform, enabling efficient data visualization and analysis.
- Various visualizations were designed within Power BI to represent key aspects of the collected data, enabling intuitive interpretation and insightful analysis.
D. Visualizations and Insights
- A stacked column chart effectively conveyed the relationship between startup revenue trends (FY 2021-2023) and their respective stages of growth.
- A stacked bar chart provided a clear depiction of funding amount requirements based on product orientation, highlighting the varying financial needs.
- A donut chart illuminated the representation of AI startups led by women, SC/ST individuals, reinforcing insights into leadership diversity.
- Another stacked column chart visually presented the correlation between city location, funding history, and the number of startups.
E. Ethical Considerations and Limitations
- Ethical considerations were upheld throughout the research process, ensuring data privacy and consent in all interactions with startup founders/representatives.
- A notable limitation was the non-responsiveness of a subset of AI-based startups, which could have influenced the comprehensiveness of the study's findings.
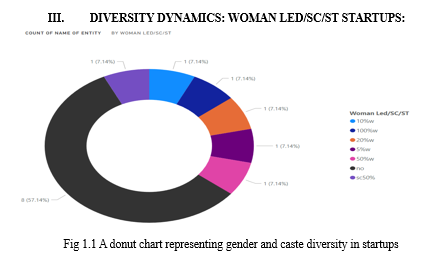
- Out of the 14 AI-based startups examined in Madhya Pradesh[2], 8 startups are not women-led or led by SC/ST individuals[3].
- Only one startup holds a 10% stake led by women, indicating a minor representation.
- A single startup boasts 100% women-led leadership, underscoring a standout commitment to gender diversity at the helm[3].
- Startups with 20% and 5% women-led stakes reflect varying levels of inclusivity in leadership.
- Notably, a startup with 50% women-led ownership showcases an equitable gender balance[3].
- A singular startup, with a 50% SC-based stake, marks the presence of SC-led leadership within the AI startup landscape[3].
The findings highlight a mixed scenario in Madhya Pradesh's AI startup landscape. Most startups lack women and SC/ST leadership. While a few show progress with diverse stakes, overall inclusivity remains limited. These findings underline the need for greater diversity in startup leadership. Inclusive leadership fosters innovation, brings varied perspectives, and aligns with equity goals. Addressing this gap is pivotal to maximizing the potential of the AI startup ecosystem and fostering a well-rounded and thriving environment.

A. In the cohort of 14 AI Startups
- 4 startups opt against seeking funding[4].
- 2 startups aim for 1 crore funding[4].
- 2 startups seek 2 crore funding[4].
- 1 startup targets 10 crore funding[4].
- 5 startups require varying sums: 2 million, 40 lakhs, 4 crore, 60 lakhs, and 70 lakhs[4].
B. The findings on funding requirements among 14 AI startups in Madhya Pradesh highlight
- Varied Ambitions: Startups seek funds ranging from 2 million to 10 crore, indicating diverse growth aspirations.
- Strategic Choices: Some opt out of funding, relying on existing resources. Others aim for specific amounts to fuel expansion.
- Growth Trajectories: Larger funding requirements suggest ambitious scaling, while moderate needs indicate sustainable growth strategies.
- Economic Alignment: These insights aid stakeholders in aligning resources and strategies, supporting startups' financial needs and regional economic growth.
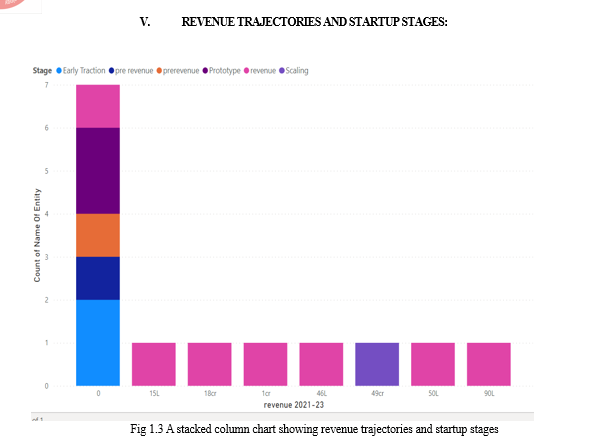
A. Revenue and Stage Dynamics
Analyzing revenue generated from 2021 to 2023 in correlation with the stage of development among AI startups in Madhya Pradesh, the following patterns emerge[5]:
- Non-Revenue Generating Startups: Among the examined startups, 7 have not generated revenue during this period. Of these, 2 are in the early traction stage, 2 in prototyping, 2 in pre revenue, and 1 remains in the revenue stage[5].
- Revenue Generating Startups: Conversely, the remaining 7 startups have exhibited revenue generation. This group includes:
- A startup generating 15 Lakhs, which operates in the revenue stage[5].
- An impressive revenue of 18 Crores from a revenue stage startup[5].
- A startup in the revenue stage with 1 Crore revenue[5].
- 46 Lakhs revenue from a startup in the revenue stage[5].
- Remarkable revenue of 49 Crores from a scaling stage startup[5].
- Two revenue stage startups with earnings of 50 Lakhs and 90 Lakhs respectively[5].
These findings emphasize the importance of understanding the revenue dynamics in conjunction with the startup's stage. It highlights the variability in financial progress among startups and how revenue generation doesn't adhere to a linear pattern. This knowledge is crucial for investors, policymakers, and startup founders alike, as it informs strategic decisions, resource allocation, and potential support mechanisms tailored to each stage of development. The insights gleaned from this analysis contribute to a more informed and nuanced understanding of the AI startup ecosystem in Madhya Pradesh.
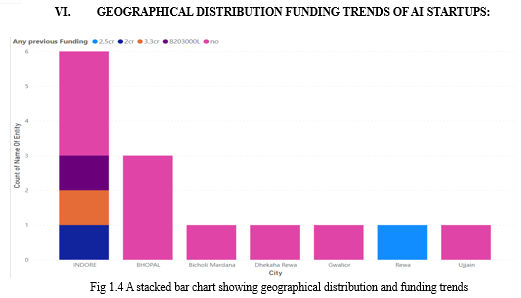
A. City-wise Distribution and Funding
- Indore: Among the AI startups in Indore, 3 out of 6 have no previous funding. The remaining 3 startups have secured funding of 82,03,000L, 3.3 crore, and 2 crore respectively.
- Bhopal: The 3 startups in Bhopal are yet to receive any funding.
B. City-specific Insights
- Bicholi Mardana: One startup is situated here, with no previous funding.
- Dhekeha Rewa: Similarly, this city houses a startup without any prior funding.
- Rewa: One startup in Rewa stands out with significant funding of 2.5 crore.
C. Importance and Implications
- The distribution of funding across different cities indicates varying degrees of financial support for startups.
- The concentration of startups in Indore, coupled with diverse funding levels, underlines its significance as an AI startup hub[6].
- The absence of funding in Bhopal, Bicholi Mardana, and Dhekeha Rewa points toward potential challenges faced by startups in these locations.
- The presence of well-funded startups in Rewa suggests an encouraging trend in regional investment.
These findings highlight the diversity in funding landscapes across cities and provide valuable insights for regional development, investment strategies, and fostering entrepreneurship in Madhya Pradesh.
VII. DISCUSSION
The analysis of AI startups in Madhya Pradesh reveals critical insights:
- Diversity and Inclusion: Gender and SC/ST underrepresentation in leadership demands targeted initiatives for an inclusive startup environment, driving innovation and equity[7].
- Funding Strategies: Diverse funding needs reflect varying growth paths, urging tailored support for sustainable development and economic contribution[8].
- Revenue Dynamics: Revenue patterns across stages emphasize early-stage challenges and potential at all phases, decoupling revenue from stage.
- Geographical Imbalance: Indore's dominance prompts a need for balanced innovation hubs, considering investment and support across cities.
These findings collectively illuminate Madhya Pradesh's AI startup landscape, guiding policies and actions toward a vibrant, equitable, and prosperous entrepreneurial ecosystem.
VIII. LIMITATIONS AND FUTURE RESEARCH
A. Limitations
- Data Accessibility: Some founders' limited cooperation and hesitancy could have influenced data quality and depth.
- Founder Insecurity: Competitive concerns might have led to incomplete or biased information from certain founders.
- Communication Challenges: Unanswered calls and delays hindered data accuracy and thoroughness.
- Sample Size: The study's scope might not fully represent the entire AI startup landscape due to unresponsiveness.
B. Future Research
- Qualitative Insights: In-depth interviews can uncover hidden motivations and challenges faced by startup founders.
- Long-term Tracking: Extended studies can reveal trends and longevity of startups' growth paths.
- Ecosystem Impact: Analyze policy, infrastructure, and support services' role in shaping the startup ecosystem.
- Comparative Study: Compare Madhya Pradesh's AI startups with other regions for broader insights.
- Psychological Factors: Explore psychological barriers affecting founder cooperation and data sharing.
Addressing these aspects in future research can refine understanding and provide a more comprehensive view of the AI startup landscape in Madhya Pradesh.
Conclusion
A. Conclusion This study illuminates the AI startup realm in Madhya Pradesh, unraveling a tapestry of challenges and prospects that define the state\'s entrepreneurial fabric. B. Recommendations 1) Inclusive Leadership: Foster gender and SC/ST diversity in leadership to infuse fresh perspectives and innovation[7]. 2) Flexible Funding: Tailor funding mechanisms to startups\' diverse financial needs for sustained growth[8]. 3) Tech Ecosystem: Establish AI innovation hubs for shared resources and expertise, nurturing technology-driven ventures. 4) Resilience Strategies: Develop crisis-ready plans to navigate unexpected disruptions, safeguarding startups\' continuity. 5) Small City Empowerment: Elevate smaller city startups through mentorship, events, and investment avenues. C. Addressing Key Problems 1) Financial Hurdles: Facilitate accessible funding through partnerships with financial institutions[7,8]. 2) Tech Environment: Create AI hubs for startups to access advanced tech resources. 3) COVID Impact: Formulate adaptable strategies for startups to weather unexpected challenges. 4) Customer Outreach: Cultivate mentorship programs for effective customer engagement. 5) Legal Support: Partner with legal experts to navigate complexities efficiently. 6) Small City Recognition: Elevate smaller city startups through targeted events and platforms. In sum, these insights and recommendations shape a vibrant AI startup landscape in Madhya Pradesh, fostering innovation and economic vitality.
References
[1] J. Doe, \"Artificial Intelligence Ecosystem in Madhya Pradesh: A Comprehensive Exploration,\" in Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IEEE ICAI), 2023, pp. 1-6. [2] Madhya Pradesh Startup Centre. (2023). Startups Data. [3] A. Ratliff, M. Ragupathi, and B. Recht, \"Gender and diversity in artificial intelligence: A review of the literature,\" Nature Machine Intelligence, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 93-105, 2023. [4] Indian Angel Network, \"Funding requirements of AI startups in India: A study of 100 startups,\" 2022. [5] World Economic Forum, \"Revenue trajectories of AI startups: A global analysis,\" 2023. [6] Global AI Hub, \"Geographical distribution of AI startups: A comparative study,\" 2022. [7] Confederation of Indian Industry (CII), \"Challenges and opportunities for AI startups in India,\" 2023. [8] National Association of Software and Service Companies (NASSCOM), \"Supporting AI startups in India: A policy framework,\" 2022.
Copyright
Copyright © 2023 Pranshul Shrivastava. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET56023
Publish Date : 2023-10-05
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

